🎭 Entity Proxies
On the inside, hass will maintain a copy of the current state as reported by Home Assistant. You are able to create references that will maintain always accurate state, allow easy service calls, and more!
📝 Creating References
Entity references provide provides a range of tools for interacting with and issuing calls.
The primary tool for obtaining references to entities is the hass.refBy.id call.
It takes in entity ids, and provides references back.
function Example({ hass }: TServiceParams) {
const mySensor = hass.refBy.id("sensor.my_special_sensor");
// that's it!
}
ID references are type checked to ensure you provided an entity that actually exists
💪 Abilities
🔮 Always Accurate State
Entity will always reflect the current state. No need to have special logic to keep track, just grab and go
const mySwitch = hass.refBy.id("switch.example");
logger.info(`current state is ${mySwitch.state}`); // on
// make changes
hass.call.switch.turn_off({ entity_id: "switch.example" });
setTimeout(() =>
// still correct
logger.info(`current state is ${mySwitch.state}`), // off
1000
);
Attributes are also accessible, with the correct attributes being listed for the specific id
logger.info({ attributes: mySwitch.attributes }, "mySwitch attributes")
Previous State
A common situation for automations is needing to know the immediate previous state of an entity. This is accessible directly in the events (below), but it is also available directly on the entity
const mySensor = hass.refBy.id("sensor.power_level");
logger.info({
current: mySwitch.state,
previous: mySwitch.previous.state
});
🎆 Event Tools
Entity references also have the ability to tap into entity change events in a variety of powerful ways.
onUpdate
The most common situation for working with states: needing to know when they change.
mySwitch.onUpdate((new_state, old_state) => {
if (old_state.state === "on" && new_state.state === "off") {
do.theThing();
}
});
// remove at any time using the return
function shortListener(callback) {
const { remove } = mySwitch.onUpdate(callback);
// next update must happen within 1s
setTimeout(() => remove(), 1000);
}
// or inside of the callback as part of logic
mySensor.onUpdate((new_state, _, remove) => {
if (Number(new_state.state) > 9000) {
logger.info(`sensor is over 9000!`);
remove();
}
})
once
Similar to the onUpdate, the once command will run your callback for a single event
mySensor.once((new_state, old_state) => {
// some logic
});
nextState
If all you want to do is wait for a state change as part of an async flow, nextState can help!
async function myComplicatedLogic() {
do.someLogic();
if (mySwitch.state === "off") {
// wait for state change
await mySwitch.nextState();
}
do.moreLogic()
}
📣 Service Calls
The last big trick for entities is the ability to issue service calls directly from the reference. This only works for service calls where the service domain matches the entity domain.
ex:
switch.my_switchcan only callswitch.turn_on|turn_off|toggle
mySwitch.turn_off();
Entity ID not required as part of the call! You are even able to pass in service params
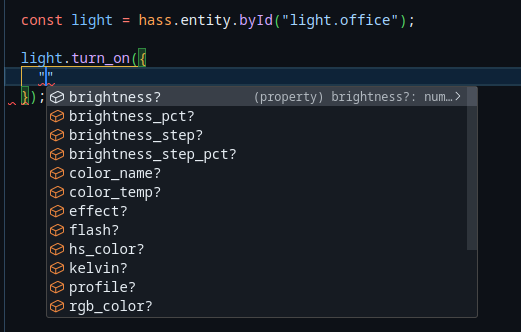
const light = hass.refBy.id("light.office");
light.turn_on({ brightness: 150 });
💒 Related Methods
Each of the following performs a lookup, optionally filtering by domain, returning an array of entity ids.
hass.idBy.area(area, ...domains)hass.idBy.device(device, ...domains)hass.idBy.label(label, ...domains)hass.idBy.floor(floor, ...domains)hass.idBy.platform(platform, ...domains)
These related methods will do the same lookup, returning an array of entity references.
hass.refBy.area(area, ...domains)hass.refBy.device(device, ...domains)hass.refBy.label(label, ...domains)hass.refBy.floor(floor, ...domains)hass.refBy.platform(platform, ...domains)